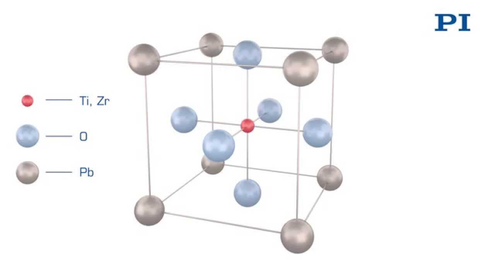
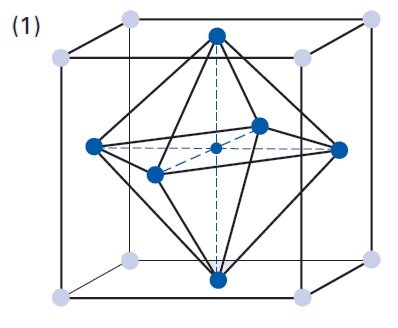
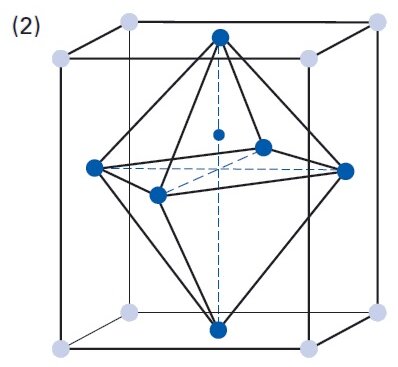
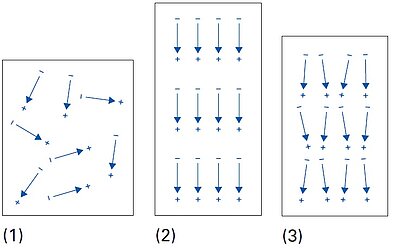
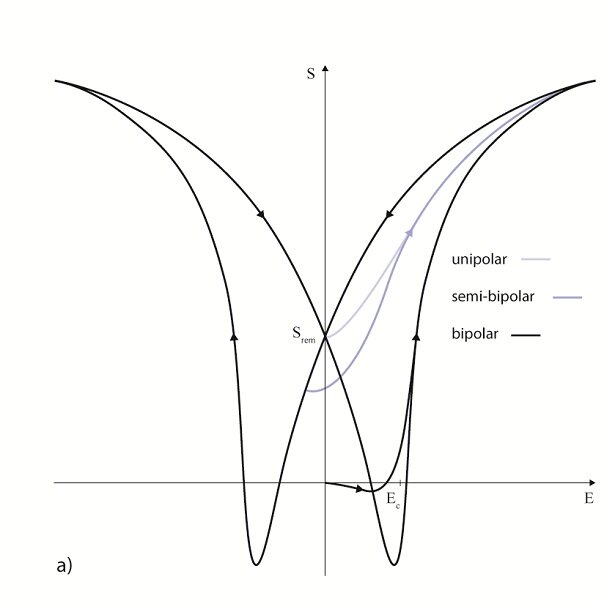
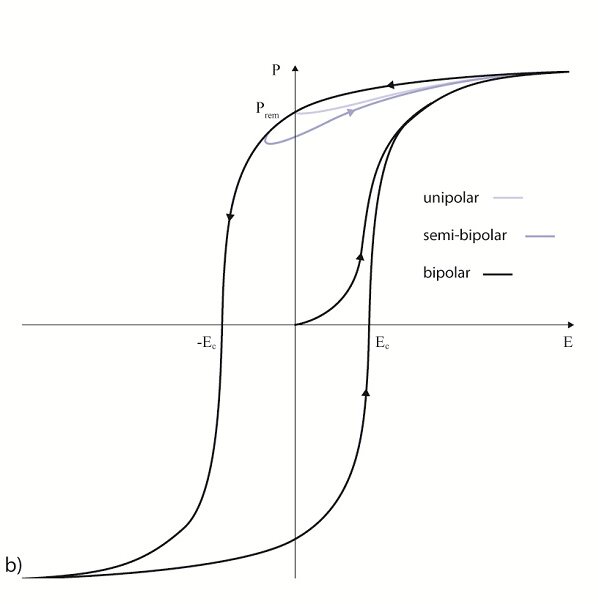
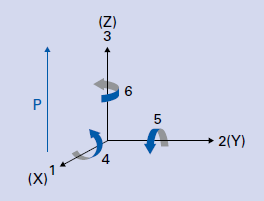
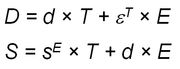The permittivity ε or the relative dielectric coefficient DC is the ratio of the absolute permittivity of the ceramic material and the permittivity in vacuum (ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 F/m), where the absolute permittivity is a measure of the polarizability in the electrical field. The dependency of the dielectric coefficient from the orientation of the electric field and the dielectric displacement is symbolized by the corresponding indices.
Examples:
ε33T DCvalue in the polarization direction when an electric field is applied in the direction of polarization (direction 3) at a constant mechanical stress (T=0: "free" permittivity)
ε11S Electrical field and dielectric displacement in the direction of axis 1, at constant deformation (S=0: "clamped" permittivity)