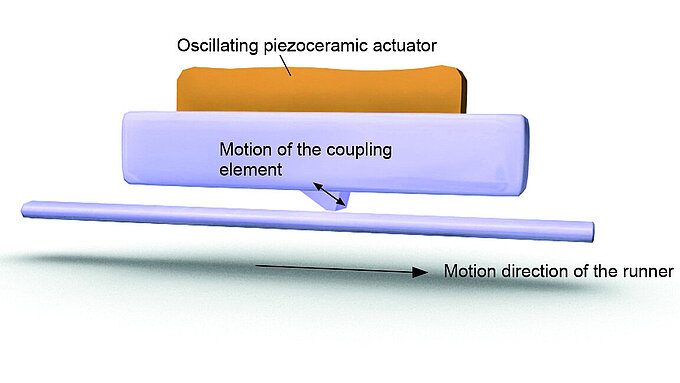
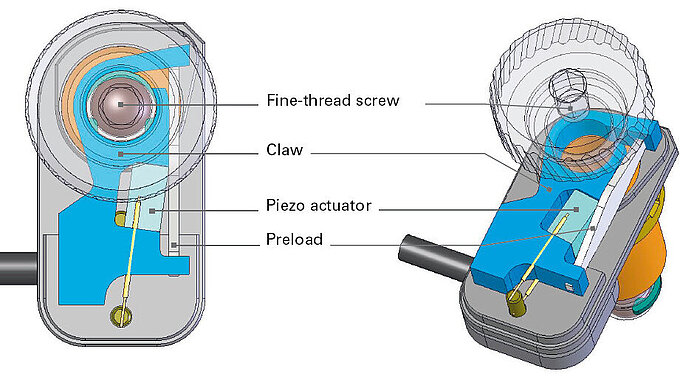
Compare the features and application ranges of piezo drive technologies. If you have queries, contact us – PI has the right solution for you!
| PICMA® / PICA | PiezoWalk® | PILine® | Q-Motion® | PiezoMike | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Principle | Piezo | Stepping | Ultrasonics | Inertia | Inertia |
| Resolution | Sub-nm | Sub-nm | Sub-µm | Sub-nm | 20 nm |
| Velocity | - | to 10 mm/s | up to several 100 mm/s | over 10 mm/s | approx. 0.2 mm/s |
| Response times in the range of a few µs | High-dynamics scan mode | Silent (very high operating frequency) | Silent (very high operating frequency) | High stability | |
| Travel Ranges | to approx. 300 µm directly and 2 mm with levere amplification | only limited by the runner length | only limited by the runner length | only limited by the runner lenght | to approx. 50 mm |
| Forces | up to 100 kN | up to 800 N (NEXLINE®) | to 40 N | to 10 N | Holding forces >100 N, Feeding force >20 N |
| High stiffness | Self-locking at rest | Self-locking at rest | Self-locking at rest | Self-locking at rest | |
| Multi-actuator drive generates stepping motion | Single-actuator drive | Single-actuator drive | Single-actuator drive | ||
| Control Mode | Analog voltage | - | High-frequency alternating voltage (sinus) | High-frequency alternating voltage (modified saw tooth) | High-frequency alternating voltage (modified saw tooth) |
| Voltage Range | 150 V (PICMA®), 1100 V (PICA®) | 55 V (NEXACT®), 500 V (NEXLINE®) | 120 V, 200 V, mini-motors considerably below | <48 V | to 100 V |
| Ideal for ... | nm-accurate positioning at high dynamics | nm-accurate positioning | Positioning with sub-µm accuracy | nm-accurate and long-term stabile positioning | Long-term stable positioning |
| Lever-amplified and guided systems | Quasi-static applications with high holding force | Fast step-and-settle | Quasi-static applications with high holding force | UHV environments | |
| Piezo scanner | Travel ranges of up to a few mm | Scan mode with high velocities | |||
| Find adjustment | Coarse and fine adjustment | Operation at constant, low velocity | |||
| Force generation | Force generation | ||||
| Active vibration insulation | Active vibration insulation | ||||
| Operation at constant, low velocity |